z-Test
Details: The null hypothesis is that x1-x2 is
normally distributed with mean 0 and variance σ12+σ22.
Typically x1-x2 is not zero, and we find the probability
that it could be that or more divergent, e.g., if |z|=2 we would calculate the area P shaded below:
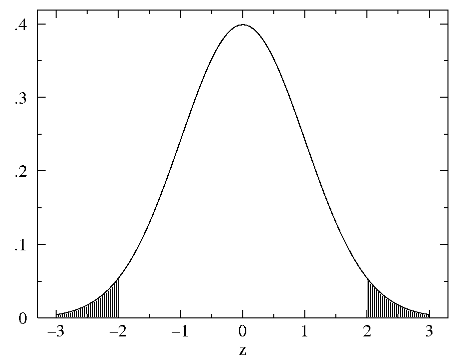
In general P can be plotted as a function of |z|
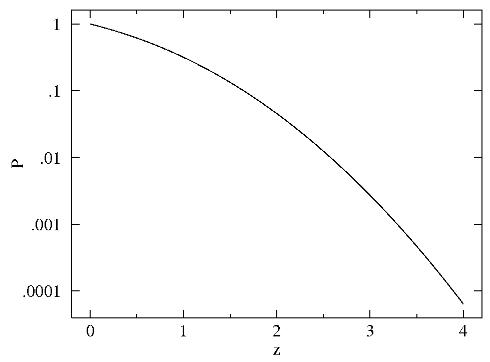
"critical" (i.e., commonly used) values
|z| P
0.674 0.5
1 0.317
1.645 0.1
1.960 0.05
2 0.0455
2.576 0.01
2.807 0.005
3 0.00270
3.291 0.001
3.481 0.0005
3.891 0.0001
4 0.0000633


